A Design of the Extrusion System for Chocolate 3D Printing
Abstract:
Food 3D printing is one of the newest developments in food design and manufacturing with great potential in both food recipe and industrial processing. Chocolate 3D printing, especially, has received investment from big companies like Hersey and 3D System. Unlike the traditional production of customized food, which requires extensive skilled labor and a long process of molding, 3D printing food allows users to design the shape by editing the digital model file.However, there are problems with the current chocolate printers that need to improve to make them popular. The first problem is that price is too high for individual users and small stores. Most people could not afford a printer that is about several thousand dollars, not to mention the expensive printer-specific material. Another problem is the ability of the printer. Some printers can only produce few default shapes set by the producer, so users do not have much freedom to print the shapes they want. This limits the ability that is supposed to be the biggest advantage of the 3D printer. And one of the biggest weaknesses of the current chocolate 3D printers is that they cannot perform tempering, a critical process in chocolate production. Without chocolate tempering, the final product chocolate will not have a smooth, glossy texture that is preferred for desserts. So the printer cannot be used for high-end dessert production.
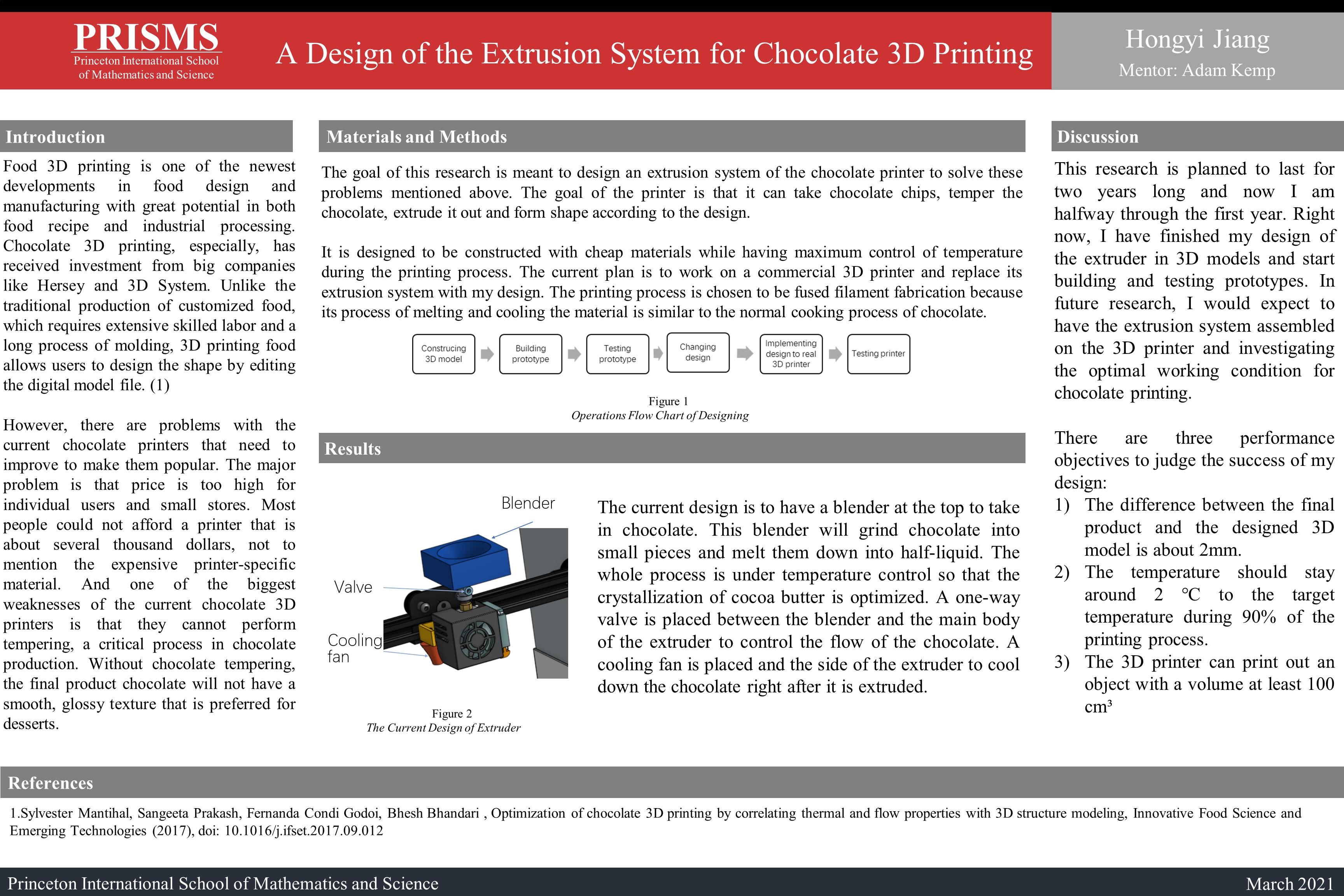
The goal of this research is meant to design an extrusion system of the chocolate printer to solve these problems mentioned above. The printer should be able to take chocolate chips, temper the chocolate, extrude it out and form shape according to the design. It is designed to be constructed with cheap materials while having maximum control of temperature during the printing process. This research is planned to last for two years long and now I am halfway through the first year. My current plan is to work on a commercial 3D printer and replace its extrusion system with my design. The printing process is chosen to be fused filament fabrication because its process of melting and cooling the material is similar to the normal cooking process of chocolate. Right now, I have finished my design of the extruder in 3D models and start building and testing prototypes. In future research, I would expect to have the extrusion system assembled on the 3D printer and investigating the optimal working condition for chocolate printing.
Bibliography/Citations:
1. Hershey to Launch the First Ever 3D Printed Chocolate Exhibit, Brian Krassenstein, Dec 17, 2014. https://3dprint.com/31758/hersheys-3d-printing-exhibit/ 2. J. I. Lipton, 3D PRINTING FOOD , FOAM AND FORCES : ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING OF EDIBLE CONSTRUCTS , CELLULAR STRUCTURES AND ACTUATORS A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Jeffrey Ian Lipton August 2015 (2015). 3. Derossi, A.; Caporizzi, R.; Ricci, I.; Severini, C. Critical Variables in 3D Food Printing; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128145647 4. Tran, J.L. 3D-Printed Food. Minnesota J. Law Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 855. 5. About Upprinting Food. Available online: https://www.upprintingfood.com/about (accessed on13 April 2020). 6. Izdebska, J.; Zołek-Tryznowska, Z. 3D food printing—Facts and future. Agro Food Ind. Hi Tech 2016, 27, 33–37. 7. L. Zhuoqun, Y. Jiazhe, PID Control of Chocolate 3D Printer Heating System 3D Printing Output Value ( Billion USD ), 298–301 (2019). 8. Loisel, C.; Keller, G.; Lecq, G.; Bourgaux, C.; Ollivon, M. (1998). "Phase Transitions and Polymorphism of Cocoa Butter". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 75 (4). pp.425–439, see Table 2 p. 426 for tempering temperatures. doi:10.1007/s11746-998-0245-y.
Additional Project Information
Project files
Research Plan:
Food 3D printing is one of the newest developments in food design and manufacturing with great potential in both food recipe and industrial processing. Chocolate 3D printing, especially, has received investment from big companies like Hersey and 3D System. (1) Unlike the traditional production of customized food, which requires extensive skilled labor and a long process of molding, 3D printing food allows users to design the shape by editing the digital model file. (2) This has huge implements for both the food industry and individual users, such as: 1. Personalising/customizing food. 3D food printing permits the creation of new geometries and offers original production ideas in food manufacturing with superior control over composition, structure, texture, and taste. (3) This is extremely helpful for delicate food, like dessert or other fine dishes. A high-end cook may use a food 3D printer to create a personalized and complex dish. 3D food printing can lead to new directions in domestic cooking or catering services. It is also useful for the individual home user. A consumer could edit and design their food at home without spending extra money on purchasing tools required for the usual cooking. 2. Eliminating redundant businesses. When 3D printing is applied to the major cooking process, many processing steps, like shaping and baking, would be unnecessary. (4) By doing so, food producers can change their focus from food production to other aspects, especially for the chocolate printer, which allows the producer to create a complex structure with minimum effort. 3. Resolving food shortage by reducing food waste and increasing the usage of existing food materials and by expanding shelf lives. 3D printing can utilize unpreserved food or low-value by-product to create a more pleasant food product. For example, the company Upprinting Food uses food waste, like bread, fruit, vegetables, as the “ink” for 3D food printers. This “ink” will later be later processed to produce food. (5) In addition to that, special designed 3D food printing material would have longer preserved time with specially tailored nutritional value. (6) Such as NASA uses dry powders for 3D printing that can have a shelf life of up to 30 years. The general process of 3D printing food is very similar to non-food 3D printing. The method varied depends on the 3D printing material, which could be divided as powder-based or fluid-based.(2) For chocolate, it’s often used as fluid during the printing process and the most common method is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). (2) FDM is a relatively cheap method and widely used in printing plastics like ABS and PLA. It starts with a digital model file like the CAD model. The model is sliced into a series of two dimensioned cross-sections. Then the 3D printer controls a heated spray head to move along the two-dimensional plane according to the data. The spray head melts the material sent from the extruder and extrudes it out of the nozzle to the workbench. After the material is cooled and solidified to form a layer, the computer modifies the height of the nozzle and prints another layer. (7) There’re also other methods for printing chocolate, like 3DP and SLS, but they require a more complex and expensive machine to operate. (2) One of the major problems in FDM, especially for material like chocolate, is that it requires precise control of the heating and cooling cycle. (7) Normally the material is heated just below the melting point before the extrusion so that it could be easily extruded and solidified. Cocoa butter, the main content that provides chocolate flavor, will crystalize to different forms under different temperatures. In the normal tempering process, chocolate is often heated to 27 ℃ for the best crystallization.(8) However, the chocolate is a mixture of various content and the melting process will vary with the recipe. The content of the recipe can affect the shape stability of 3D printed object. Research shows that the increase of butter concentration in the cookie will decrease the shape stability. The material won’t be able to hold form if there’s to much butter content. The increase of yolk could help to increase the shape stability in width and length of the object, while decreasing the stability in height. (2) A similar phenomenon has been found in chocolate, that chocolate with higher cocoa fat will melt at a lower temperature. (8) But the detailed mechanism is not yet discovered. To build a 3D printer, we start by creating the 3D model of the printer. Then we construct a small prototype and test the design. We keep repeating this process until we are satisfied with this prototype. After that, we buy a small 3D printer, and we replace its extrusion system with ours. We start testing it by printing out different shapes. Then configure the setting base on the testing results. After completing the printer, we may start improving it as a commercial product.
Questions and Answers
1. What was the major objective of your project and what was your plan to achieve it?
a. Was that goal the result of any specific situation, experience, or problem you encountered?
b. Were you trying to solve a problem, answer a question, or test a hypothesis?
The goal of this project is to build a 3D printer that can print with chocolate and perform tempering. The printer should be cheap, user-friendly, and attractive to customers.
2. What were the major tasks you had to perform in order to complete your project?
a. For teams, describe what each member worked on.
To build a chocolate 3D printer, we have to understand the mechanism of the 3D printer and the special feature of chocolate. Then we start by creating the 3D model of the printer. Then we construct a small prototype and test the design. We keep repeating this process until we are satisfied with this prototype. After that, we buy a small 3D printer, and we replace its extrusion system with ours. We start testing it by printing out different shapes. Then configure the setting base on the testing results. After completing the printer, we may start improving it as a commercial product.
3. What is new or novel about your project?
a. Is there some aspect of your project's objective, or how you achieved it that you haven't done before?
b. Is your project's objective, or the way you implemented it, different from anything you have seen?
c. If you believe your work to be unique in some way, what research have you done to confirm that it is?
there are problems with the current chocolate printers that need to improve to make them popular. The major problem is that price is too high for individual users and small stores. Most people could not afford a printer that is about several thousand dollars, not to mention the expensive printer-specific material. And one of the biggest weaknesses of the current chocolate 3D printers is that they cannot perform tempering, a critical process in chocolate production. Without chocolate tempering, the final product chocolate will not have a smooth, glossy texture that is preferred for desserts. The goal of this research is meant to design an extrusion system of the chocolate printer to solve these problems mentioned above. The printer should be able to take chocolate chips, temper the chocolate, extrude it out and form shape according to the design.
4. What was the most challenging part of completing your project?
a. What problems did you encounter, and how did you overcome them?
b. What did you learn from overcoming these problems?
The major problem is that I do not have any previous knowledge about anything related to 3D printing or chocolate. There are so many things out there and I don't where to start. I have to learn everything from the most basic one. I need to learn what is food 3D printing and how others have done it. I need to know the special features of chocolate. And I have learned how to build a 3D model to show my design.
5. If you were going to do this project again, are there any things you would you do differently the next time?
If I can do this project again, I will target a more specific topic. This time I spent a lot of time getting started because my topic is too general. Next time I will try to narrow it down to a small area like "the temperature control in 3D printer".
6. Did working on this project give you any ideas for other projects?
I think I should investigate the small subtopic of this project first. Because this time the project seems to be too big for me to handle.
7. How did COVID-19 affect the completion of your project?
Due to the COVID-19, my school was closed and we only have online courses. So I don't have a place and equipment to build stuff. My initial goal was to build a 3D printer and use it to print different objects. But now I can only work on the design of the 3D printer.